Class 12th Chemistry CH- SOLUTION Intext Question Solution Part-1 2022-23
NCERT Textbook Questions
formula's
NCERT Textbook Questions
NCERT Intext Questions
Q. 1. Calculate the mass percentage of benzene (C6H6) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) if 22 g of benzene is dissolved in 122 g of carbon tetrachloride.
Q. 2. Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride?
Q. 3. Calculate the molarity of each of the following solutions:
(a) 30 g of Co(NO3)2. 6H2O in 4.3 L of solution
(b) 30 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4 diluted to 500 mL
Q. 4. Calculate the mass of urea (NH2CONH2) required in making 2.5 kg of 0.25 molal aqueous solution.
Ans. Mass of required aqueous solution = 2.5 kg = 2500 g
0.25 molal aqueous solution of urea means 0.25 mole of urea is dissolved in 1000 grams of water.
Mass of water = 1000 g
Moles of urea = 0.25 mol
Molar mass of urea (H2NCONH2) = 4 × 1 + 2 × 14 + 1 × 12 + 1 × 16 = 60 g mol–1
Mass of urea = Number of moles of urea × Molar mass of urea\ Mass of 0.25 moles of urea = 0.25 mol × 60 g mol–1 = 15 g
Mass of solution = 1000 g + 15 g = 1015 g
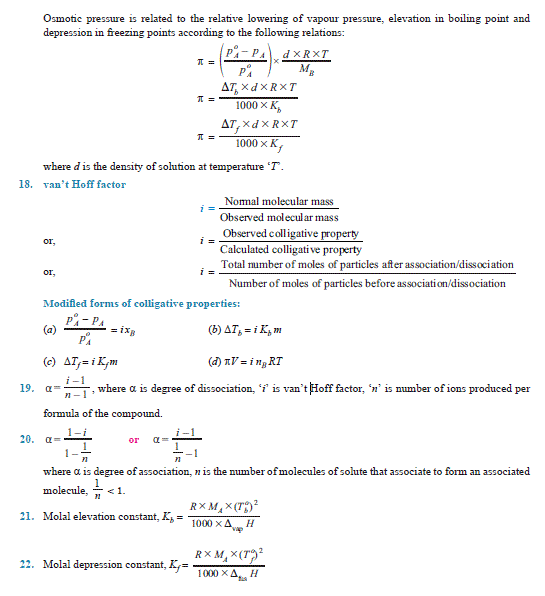
1015 g of aqueous solution contains urea = 15 g
therfore, 2500 g of aqueous solution will require urea =15 g/1015 g× 2500 g = 36.95 g
Q. 5. Calculate (i) molality (ii) molarity and (iii) mole fraction of KI if the density of 20% (mass/mass) aqueous KI is 1.202 g mL–1.
Ans. 20% (mass/mass) aqueous KI solution means that
Mass of KI = 20 g
Mass of solution = 100 g
Mass of solvent (water) = 100 – 20 = 80 g
Q. 6. H2S, a toxic gas with rotten egg-like smell, is used for qualitative analysis. If the solubility of H2S in water at STP is 0.195 m, calculate Henry’s law constant.
Ans. 0.195 m aqueous solution of H2S means 0.195 mole of H2S is dissolved in 1000 g of water.
Q. 7. Henry’s law constant for CO2 in water is 1.67 × 108 Pa at 298 K. Calculatethe quantity of CO2 in 500 mL of soda water when packed under 2.5 atm CO2 pressure at 298 K.
= 1.834 g
Q. 8. The vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B are 450 and 700 mm Hg respectively at 350 K. Find out the composition of the liquid mixture if the total vapour pressure is 600 mm Hg. Also find the composition of the vapour phase.
Q. 9. Vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.8 mm Hg. 50 g of urea NH2CONH2 is dissolved in
850 g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution and its relative lowering.
Q. 10. Boiling point of water at 750 mm Hg is 99.63ºC. How much sucrose is to be added to 500 g of water
such that it boils at 100ºC?
Ans. Molecular mass of sucrose, (C12H22O11), MB = 12 × 12 + 22 × 1 + 11 × 16 = 342 g mol–1
Mass of water = 500 g
Elevation in boiling point, deltaTb = 100 °C – 99.63 °C = 0.37 °C = 0.37 K
Q. 11. Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid (Vitamin C, C6H8O6) to be dissolved in 75 g of acetic acid to lower its melting point by 1.5ºC. Kf = 3.9 K kg mol–1. [CBSE 2020 (56/1/1)]
Ans. Molecular mass of ascorbic acid, MB = 6 × 12 + 8 × 1 + 6 × 16 = 176 g mol–1
Q. 12. Calculate the osmotic pressure in pascals exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of polymer of molar mass 185,000 in 450 mL of water at 37ºC.
PLEASE SEARCH
NCERT EXERCISE question solution in PART = 2











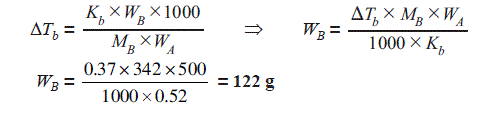



.png)




Comments
Post a Comment